Two New Publications on Digital Archaeology at Kaymakçı
Gygaia Projects
We are pleased to share news that two new publications on digital archaeology at Kaymakçı have just appeared in Open Archaeology. See below for details!
Catherine B. Scott, Christopher H. Roosevelt, Gary R. Nobles, and Christina Luke
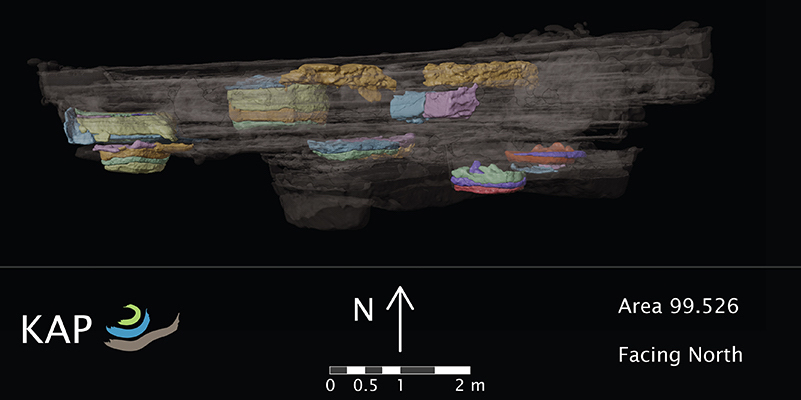
Abstract: Digital technologies have been at the heart of fieldwork at the Kaymakçı Archaeological Project (KAP) since its beginning in 2014. All data on this excavation are born-digital, from textual, photographic, and videographic descriptions of contexts and objects in a database and excavation journals to 2D plans and profiles as well as 3D volumetric recording of contexts. The integration of structure from motion (SfM) modeling and its various products has had an especially strong impact on how project participants interact with the archaeological record during and after excavation. While this technology opens up many new possibilities for data recording, analysis, and presentation, it can also present challenges when the requirements of the recording system come into conflict with an archaeologist’s training and experience. Here, we consider the benefits and costs of KAP’s volumetric recording system. We explore the ways that recording protocols for image-based modeling change how archaeologists see and manage excavation areas and how the products of this recording system are revolutionizing our interaction with the (digital) archaeological record. We also share some preliminary plans for how we intend to expand this work in the future.
Filling the Void in Archaeological Excavations: 2D Point Clouds to 3D Volumes
Gary R. Nobles and Christopher H. Roosevelt

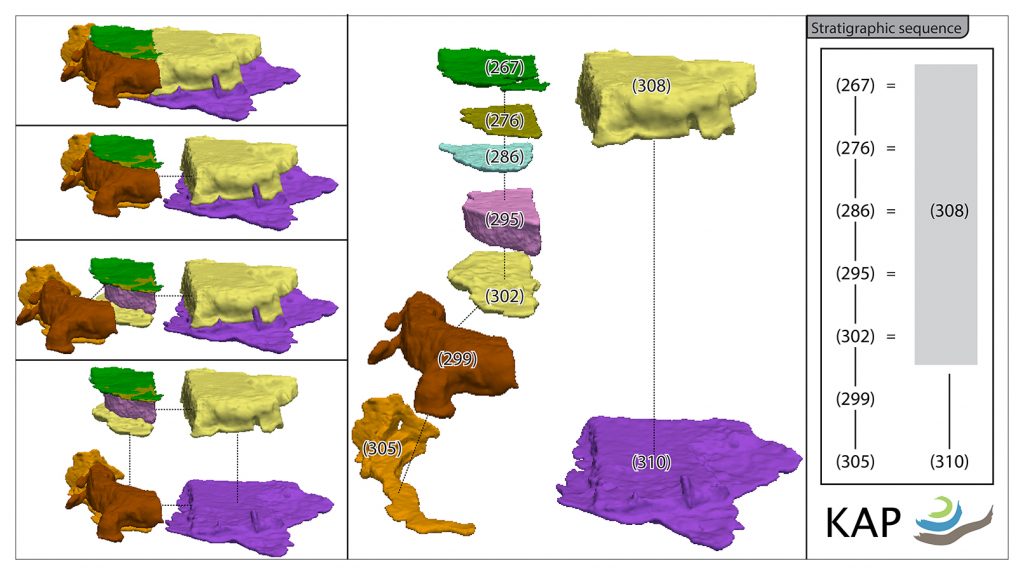
Abstract: 3D data captured from archaeological excavations are frequently left to speak for themselves. 3D models of objects are uploaded to online viewing platforms, the tops or bottoms of surfaces are visualised in 2.5D, or both are reduced to 2D representations. Representations of excavation units, in particular, often remain incompletely processed as raw surface outputs, unable to be considered individual entities that represent the individual, volumetric units of excavation. Visualisations of such surfaces, whether as point clouds or meshes, are commonly viewed as an end result in and of themselves, when they could be considered the beginning of a fully volumetric way of recording and understanding the 3D archaeological record. In describing the creation of an archaeologically focused recording routine and a 3D-focused data processing workflow, this article provides the means to fill the void between excavation-unit surfaces, thereby producing an individual volumetric entity that corresponds to each excavation unit. Drawing on datasets from the Kaymakçı Archaeological Project (KAP) in western Turkey, the article shows the potential for programmatic creation of volumetric contextual units from 2D point cloud datasets, opening a world of possibilities and challenges for the development of a truly 3D archaeological practice.
Look forward to more posts from Gygaia Projects soon!